Suspension Therapy
Suspension therapy is the exercise unit or a frame which is also known as Guthrie smith frame in which muscles are strengthened by using ropes, pulleys, and slings.
The effect of suspension on movement from the resting position is similar to that of an inclined re-education board which supports the limb during movement up the incline but differs from it in in that, in suspension friction is virtually eliminated.
Suspension functions as not only to eliminate frictional resistance from the moving body part but also promotes a feeling of weightlessness such as experienced by buyoncy in the hydrotherapy pool.
Uses
It is mainly used to allow the muscle to contract actively in the gravity eliminated position or against gravity and subsequently improve the muscle strength, joint range of motion and decrease the pain and muscle spasm.
Parts of suspension therapy
- Suspension frame - Fixed point
- Slings
- Single slings
- Double slings
- Three ring slings
- Head sling
- Clips and hooks
- Carabine clip
- Dog clip
- S hook
- The wooden cleat
- The supporting ropes
- Single rope
- Double rope or Double pulley rope
- Single pulley rope
1. Suspension frame
It's made of stainless steel or steel with a plastic coating. The 5-centimeter metal mesh is displayed on the top and head-end sides, leaving the other sides exposed.
2. Slings
These are used mainly to support the limbs, and the each end is attached with D ring. Slings are made up of canvas. Common types of slings are as follows:
i. Single slings
These are placed usually under the joints to support them. if single sling is used as figure of eight it supports the proximal and distal parts of the joint (for example to support the peripheral joints such as ankle and wrist).
ii. Double slings
Generally used to support the trunk and pelvis.
iii. Three ring slings
Three D rings are attached with the sling so these are known as three ring slings. These slings are used to support wrist, hand, ankle and foot. The length around 71cm and width 3-4 cm is commonly used. Two D rings attached at both ends to make two loopes and one D ring is at the centre which is attached to the dog clip.
iv. Head sling
As the name suggests it is used to support the head. The central part of the sling splits and divided into two halves which are stitched together at an angle to create a central slit.
3. Clips and hooks
The clips are used to attach the ropes with the slings while hooks are suspended on the suspension unit (fixed point) with ine end and other end is attached with pulley or rope, generally an 'S' shaped hook is used. The either end of 'S' hook is used according to the fixed point. Common clips and hooks are: Carabiner clip, Dog clip and S hook.
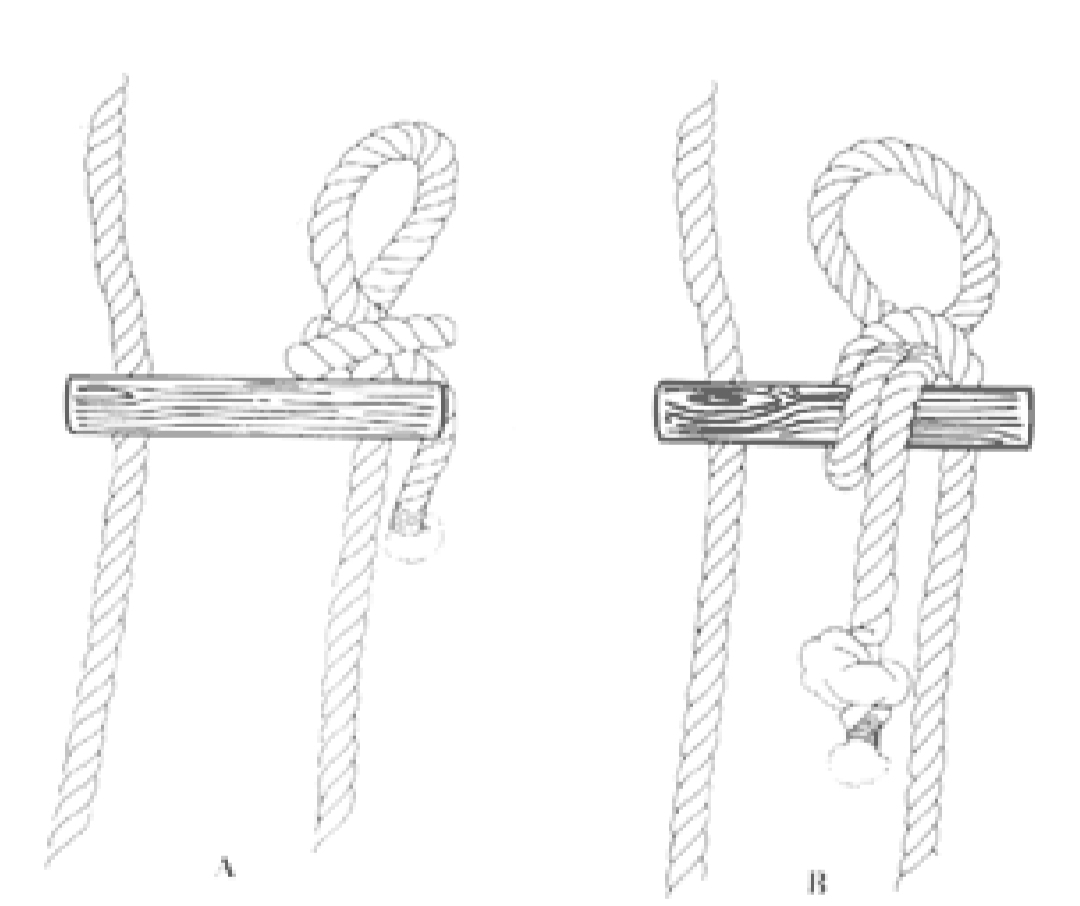
4. The wooden cleat
It is made up of a wooden and have two or three holes. The cleat is used to alter the length of the rope. To alter the length of rope the cleat is held in horizontal position and to hold the rope by its frictional resistance the cleat is held in oblique position.
The supporting ropes
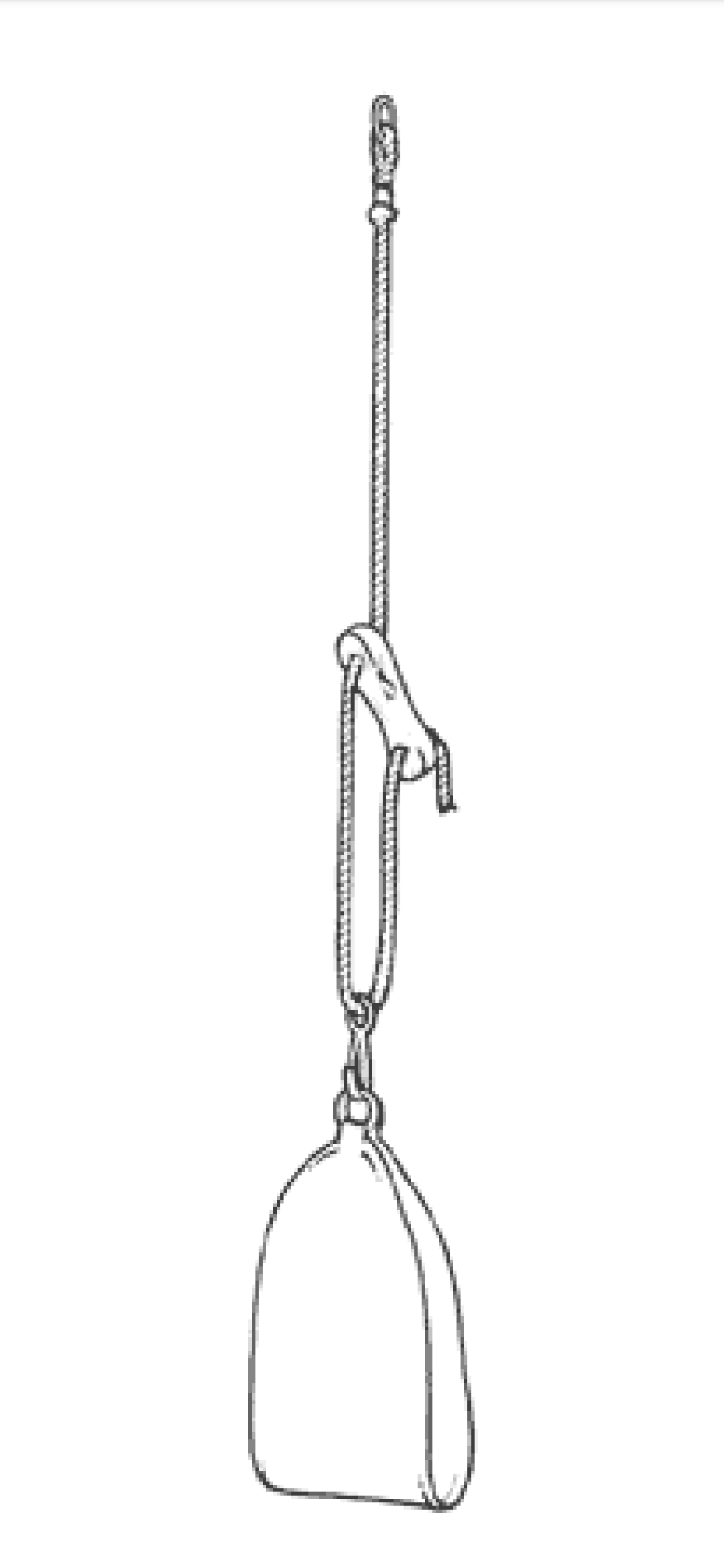
i. Single rope
The one end of the single rope is tied with the 'S' hook or D ring. The other end passage though the cleat, dog clip and takes U turn to pass through the other end of the cleat and then it is knotted. The free end is knotted in such a manner that a tug on it enables quick release.
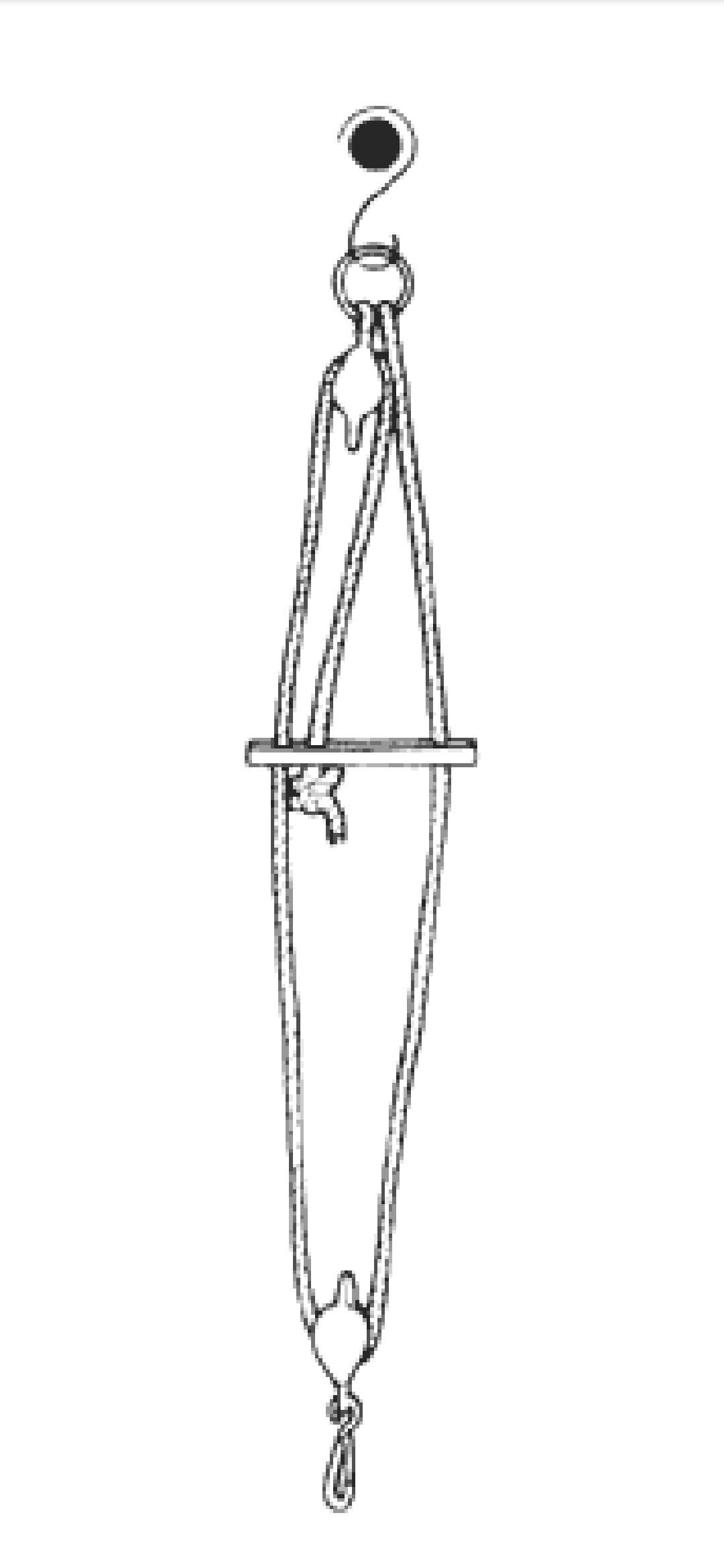
ii. Double pulley rope
The one end of the rope is attached with the ring or clip same as single rope. The other free end of rope passes through the one end of cleat, rounds a lower pulley wheel (the wheel is attached with the dog clip) then back through the other end of the cleat over passes down again through the centre hole of the cleat where it is finally knotted.
Double rope is used to suspend the pelvis, thorax, and both thighs.
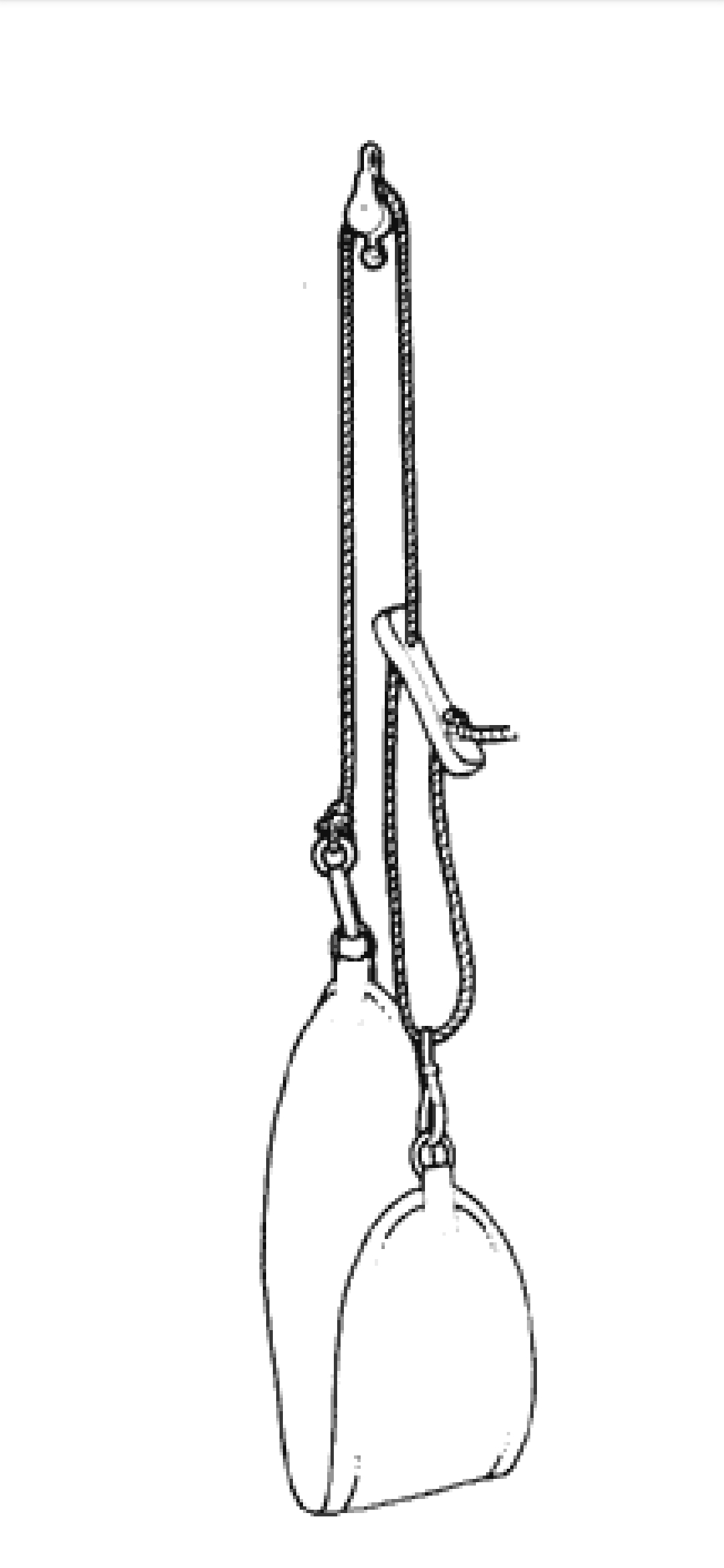
iii. Single pulley rope
The one end of the rope is attached with the dog clip or D ring at the sling. The other free end of the rope passage up over the wheel of a pulley then down through one end of the cleat and through the dog clip of the sling. Finally it takes U turn to the other end of the cleat where it is knotted. This type of rope is used for three dimensional movements of a limb i.e. abduction or adduction with flexion or extension and medial or lateral rotation.
Types of suspension
Axial fixation
The fixation point for all ropes which are attached with the slings to support the moving limb is located immediately above the centre of the moving joint.
Vertical fixation
The fixation point for all ropes are located over the center of gravity of the moving segment.
Pendular suspension
It is a type of suspension in which the axis of axial suspension is changed to apply resistance to the moving limb.
The axis is shifted away from the axial fixation of the hip joint (e.g. patient lies in side lying the axis of the suspension is shifted posterior to the hip joint to strengthen the flexors of the hip joint.)
SHARE:


- A B Desai (1979)., The suspension therapy.
- M. Dena Gardiner., The principles of exercise therapy.
| Name | : | Deva senathipathi |
| Qualifications | : | Physiotherapist |





