Biomechanics of running
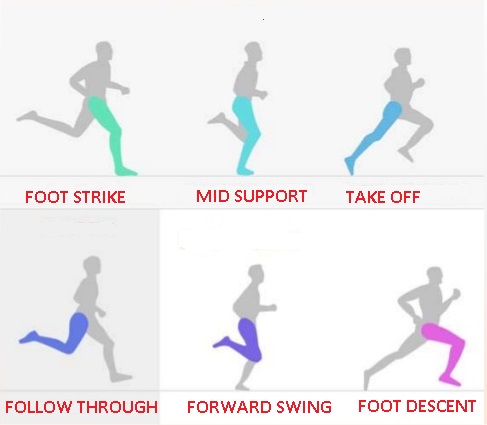
Phases of Running
- Support Phase
Foot strike
Start from initial contact of the foot with ground and continuous until complete contact of the plantar surface of the foot with the ground (plantigrade).
Mid support
From full contact of the plantar surface of the foot and continuous until heel starts to leave the ground.
Take off
Start from heel start to leave the ground to toes are completely lift off from the support surface.
- Flight / Recovery phase
Follow through
It is from end of the take off to stoppage of backward motion of the limb.
Forward swing
Begins with forward motion from the end of backward motion of follow through and it stops when foot reaches most forward position.
Foot descent
Start at the point of maximal hip flexion and continuous until foot strikes the ground.
- Airborne period
In this period, neither of the foot contact the ground. Airborne period increases acceleration of the body which causes ground reaction force 3 times greater than walking during heel/foot strike. Newton's second law states that force equals mass times acceleration.
Biomechanical analysis
Joint ROM
Stride length
Foot placement
Muscle activity
Hip joint
- Rectus femoris acts at early support phase and diminish at end of support phase.
- Gluteus maximus - Early in foot descent phase to first 40% of support phase.
- Adductors - Acts throughout the support phase.
- Quadriceps - Early support phase.
- Hamsring - Before foot strike to extension of limb during end of support phase.
- Tibialis anterior and gastroc co-contract and stabilizes ankle during foot strike.
| Running phase | Joint | Motion |
|---|---|---|
| Foot strike to mid support | Hip Knee Ankle | 45° - 20° Flexion at mid support. 20°-40° Flexion by mid support 5° Plantar flexion to 10° Dorsiflexion |
| Mid support to take off | Hip Knee Ankle | 20° Flexion to 5° Extension 40°-15° flexion 10°-20° dorsiflexion |
| Follow through | Hip Knee Ankle | 5°-20° Hyperextension 15°-5° Flexion 20°-30° Plantar flexion |
| Forward swing | Hip Knee Ankle | 20°-65° Flexion 5°-130° Flexion 30° Plantar flexion to 0° |
| Foot descent | Hip Knee Ankle | 65°-40° Flexion 130°-20° Flexion 0°-5° dorsiflexion to 5° plantar flexion. |
Stride length increases with increase in speed of running. variations can occur with uphill run or downhill run. Stride length decreases with uphill running and stride length increases with downhill running.
Increased running performance is proportional to increase in stride rate and not from stride length (landry & Zebas).
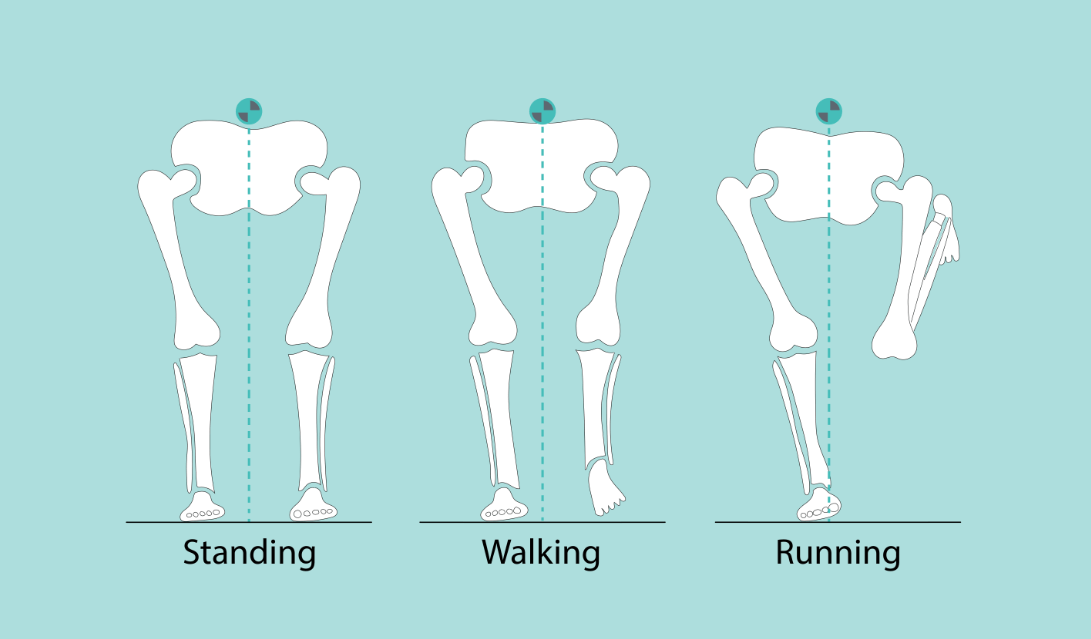
Base of support (length between two heels) is 2 to 4 inches during walking and it is 0 during running. Because of functional limb varus.
Functional limb varus is defined as the angle between the bisection of the lower leg and the floor. It causes lateral shifting of pelvis and over pronation of foot during running. Later, this increase in forefoot pronation during running may cause soft tissue injuries.
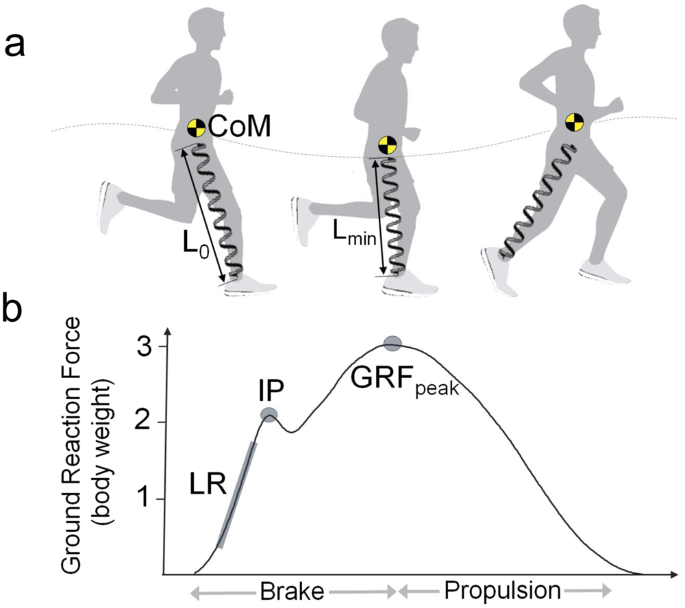
Running kinetics
Vertical component of Ground Reaction Force is 2 to 3 times of body weight during running and jogging. Adequate midsole cushioning in a running shoe is necessory to help the body attanuate or lessen the effect of these impact forces.
Shock attanuation model: Simultaneous movement(flexion) of hip knee and ankle shortens the limb. it causes eccentric contraction of muscles which in turn reduces the impact forces.
Pathology
SHARE:


- James E. Zachazeski, David J magee., Athletic injuries and rehabilitation.
| Name | : | Deva senathipathi |
| Qualifications | : | Physiotherapist |





